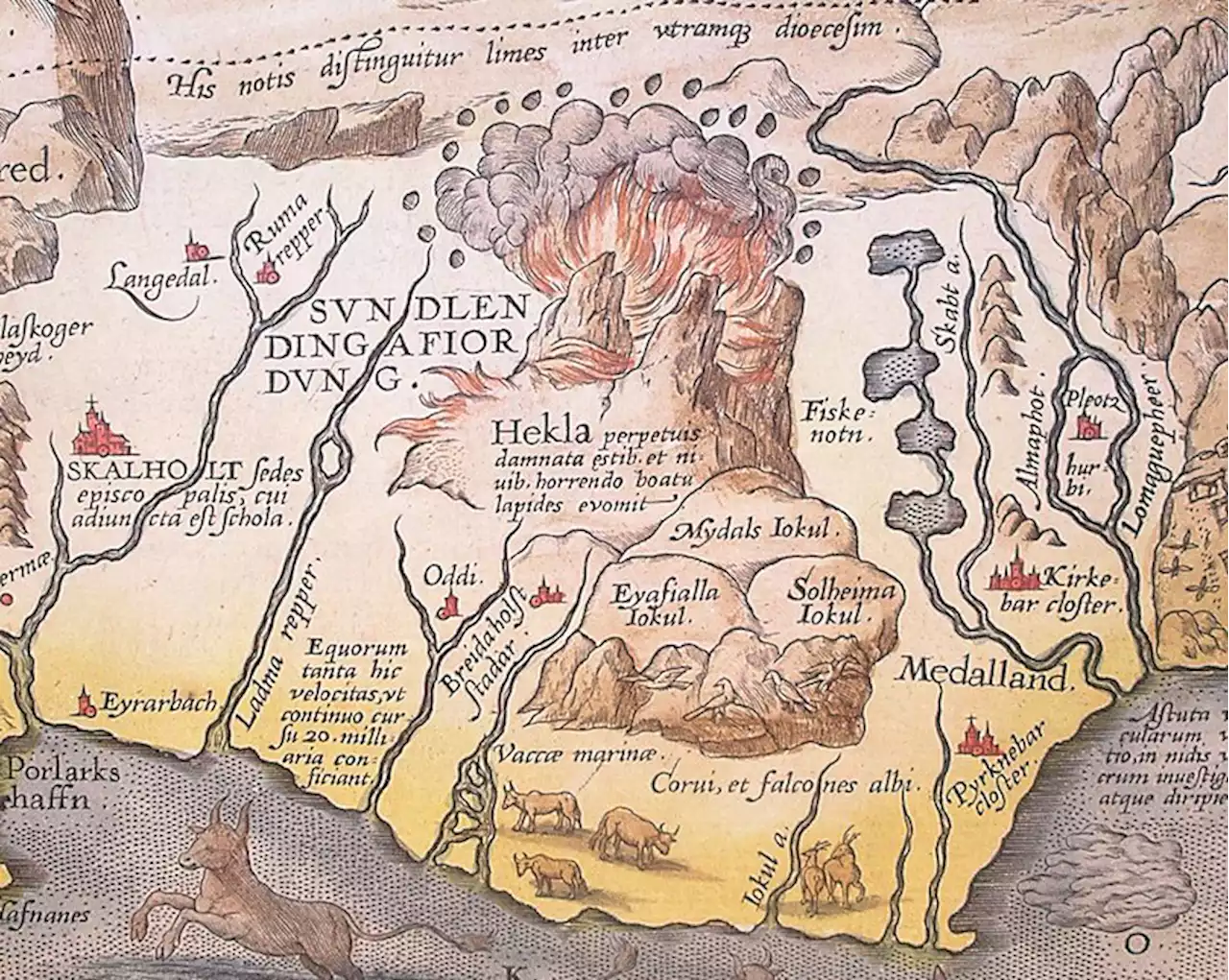
🔄From The Archive: No zombies here, just some ancient natural disasters.
The eruption of the Icelandic volcano Hekla may have led to the collapse of multiple thriving Bronze Age societies. Life, as they say, goes on. Until one day it doesn’t. For ancient societies, without the means to predict natural disasters, destruction could often come suddenly and completely by surprise. Below are four of the most devastating natural events in recorded human history, and the societies that they wiped off the map.
. The destruction would have been virtually instant, eradicating all life on the island. Today, you can stand on top of cliffs 1,000 feet high that form the bowl of the Santorini crater, and imagine the vast tsunamis that rippled across the sea, the sky blackening overhead. Minoan settlements on nearby Crete were swept away.
The heavy buildings of Thonis were built on soft coastal ground made of clay. Loose, sandy soil of this kind, when saturated with water and struck by earthquake tremors, can undergo a sudden change that makes it behave like liquid. This is still a challenge to modern architects in earthquake-prone areas like Taiwan.
Argentina Últimas Noticias, Argentina Titulares
Similar News:También puedes leer noticias similares a ésta que hemos recopilado de otras fuentes de noticias.
 $250K offered to decode ancient Roman scrollsFormer GitHub CEO Nat Friedman is helping fund $250,000 in prizes aimed to decode ancient Roman scrolls.
$250K offered to decode ancient Roman scrollsFormer GitHub CEO Nat Friedman is helping fund $250,000 in prizes aimed to decode ancient Roman scrolls.
Leer más »
Ancient DNA upends European prehistory | Science | AAAS
Leer más »
 Ancient Structures in The Arabian Desert Reveal Fragments of Mysterious RitualsWe might be getting closer to understanding why hundreds of large stone structures were built across the deserts of northwest Saudi Arabia thousands of years ago.
Ancient Structures in The Arabian Desert Reveal Fragments of Mysterious RitualsWe might be getting closer to understanding why hundreds of large stone structures were built across the deserts of northwest Saudi Arabia thousands of years ago.
Leer más »
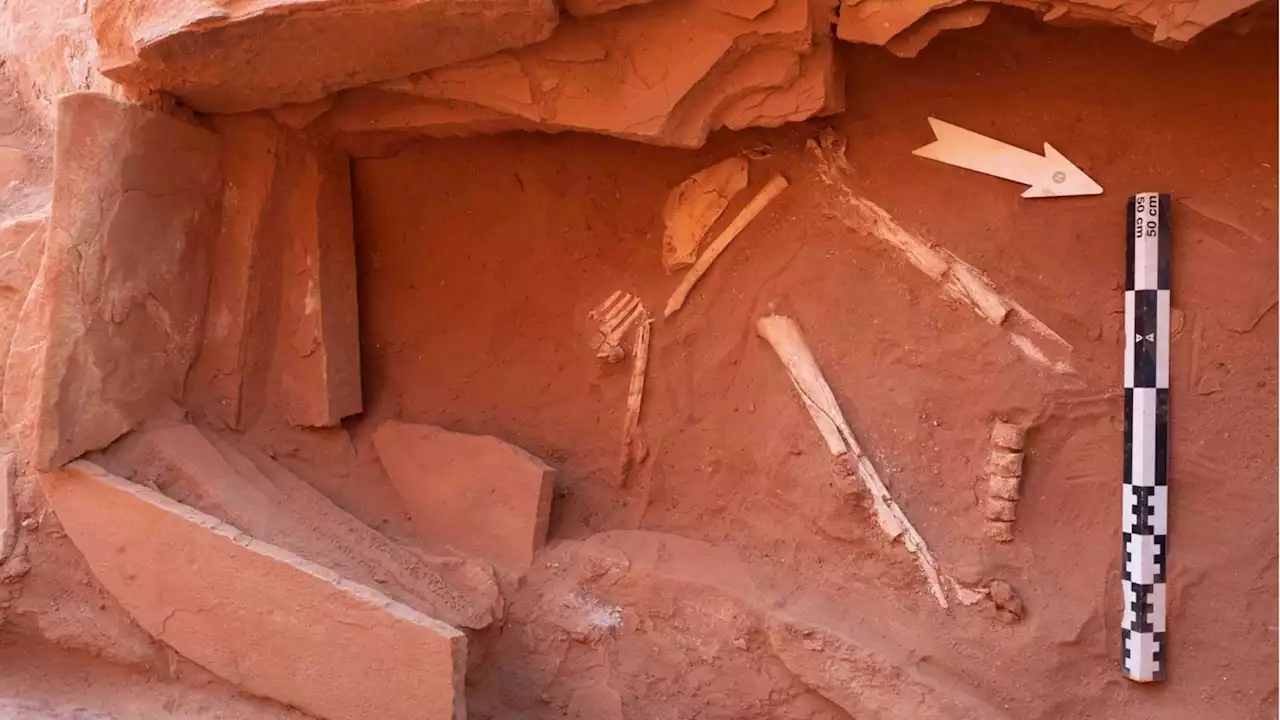 Enigmatic stone structures of Saudi Arabia reveal ancient customsNew conclusions have arisen from 'the ritual deposition of animal horns and upper cranial element within the mustatil.'
Enigmatic stone structures of Saudi Arabia reveal ancient customsNew conclusions have arisen from 'the ritual deposition of animal horns and upper cranial element within the mustatil.'
Leer más »
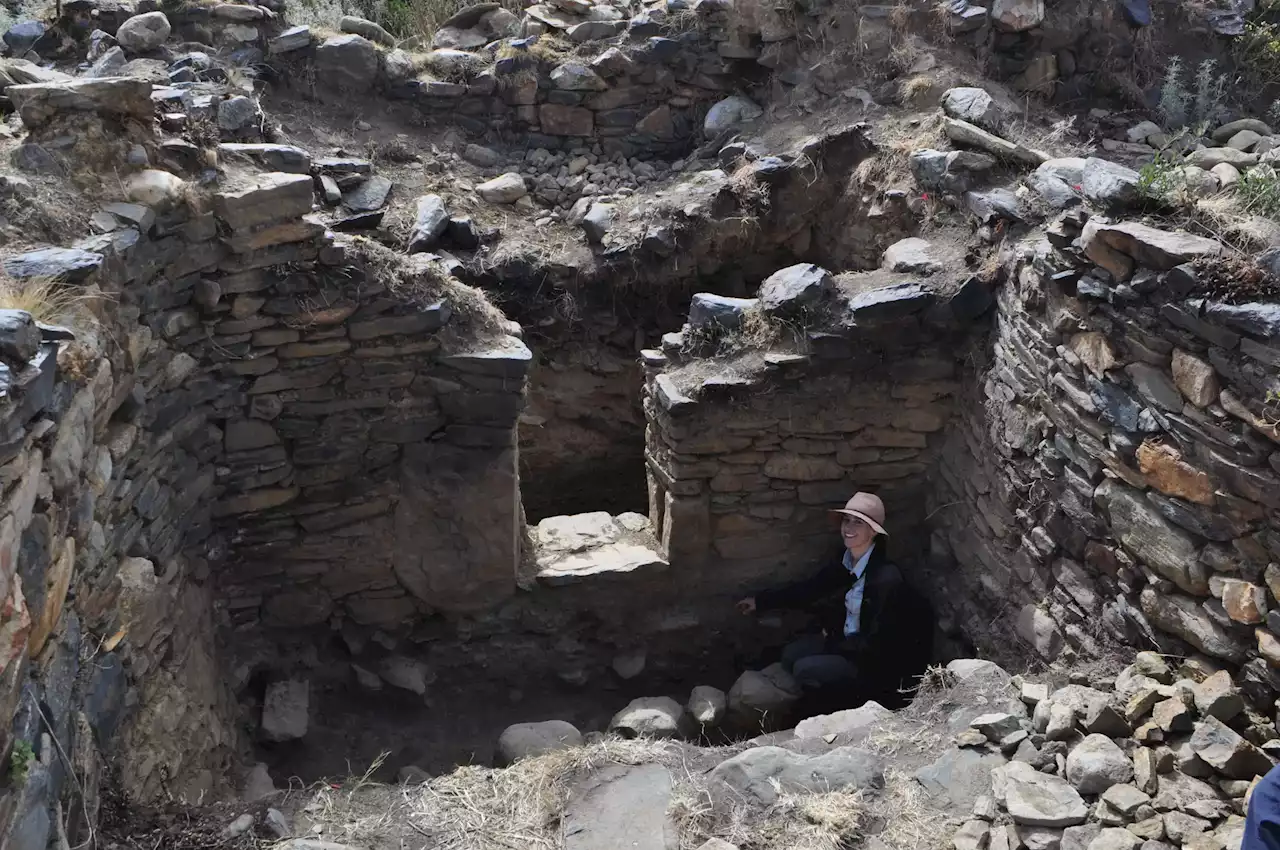 Lasers and Chemistry Reveal How How an Ancient Empire FunctionedThe Wari Empire, Peru's earliest major civilization, spanned over a thousand miles across the Andes Mountains and the coastal region from 600-1000 CE. The remnants of their pottery provide valuable insights for archaeologists seeking to understand how the ancient empire functioned. A recent study
Lasers and Chemistry Reveal How How an Ancient Empire FunctionedThe Wari Empire, Peru's earliest major civilization, spanned over a thousand miles across the Andes Mountains and the coastal region from 600-1000 CE. The remnants of their pottery provide valuable insights for archaeologists seeking to understand how the ancient empire functioned. A recent study
Leer más »
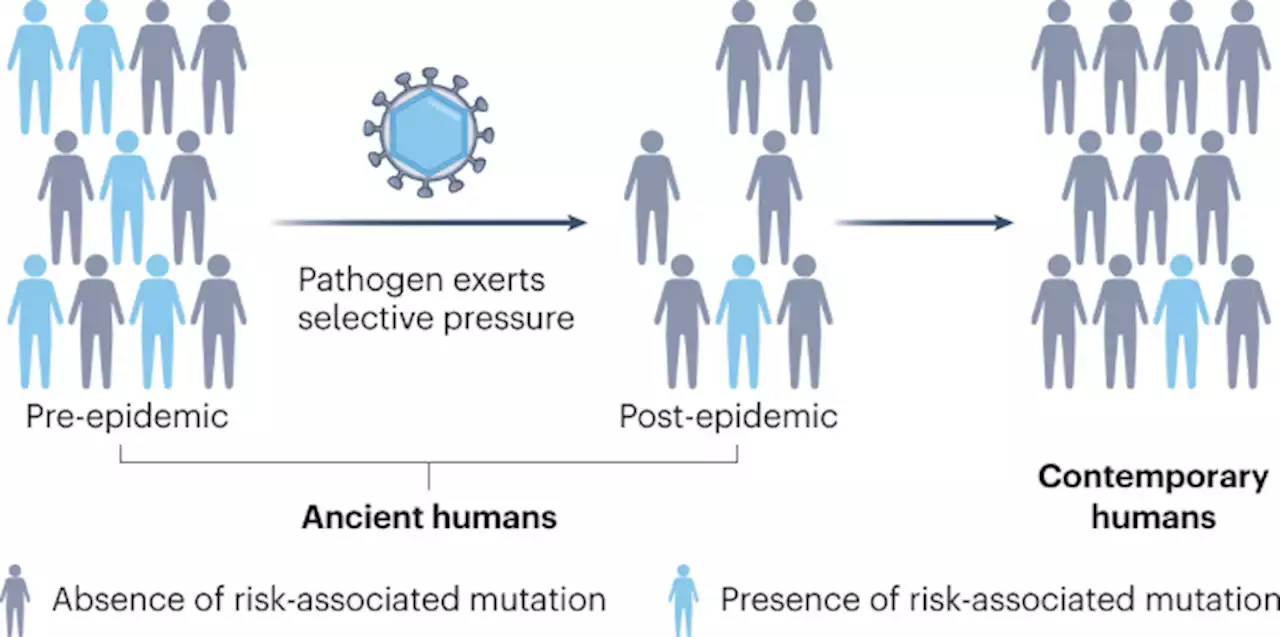 Ancient DNA as a tool for medical research - Nature MedicineAncient DNA as a tool for medical research. Comment from QuintanaMurci and colleagues on how paleogenomics can help make sense of medicine. JeremyChoin GaspardKerner CNRS institutpasteur
Ancient DNA as a tool for medical research - Nature MedicineAncient DNA as a tool for medical research. Comment from QuintanaMurci and colleagues on how paleogenomics can help make sense of medicine. JeremyChoin GaspardKerner CNRS institutpasteur
Leer más »